FOR LUTEAL PHASE SUPPORT1




Adverse Event reporting information can be found in footer
Request a Meeting
Find out how the two compared in this retrospective study to evaluate pregnancy outcomes
Trial type: retrospective cohort study
Participants: 544 women undergoing IVF at a tertiary referral infertility centre
Primary outcome: ongoing pregnancy rate
Secondary outcomes: rates of clinical pregnancy and pregnancy loss (chemical and miscarriage), serum progesterone levels during the luteal phase and early pregnancy
Comparator agents: Endometrin® (100 mg vaginal progesterone tablets; marketed as Lutigest® in the UK) (n = 145) and 100mg intramuscular progesterone injections (n = 399)
Protocol: long GnRH agonist
Ongoing pregnancy rate: Lutigest® not statistically different to IM progesterone [odds ratio (95% confidence interval): 1.0675 (0.7587-1.5020)]
Rates of total pregnancy loss: Lutigest® not statistically different to IM progesterone [odds ratio (95% confidence interval): 1.0775 (0.7383-1.5727)]
Mean serum progesterone levels during luteal phase: Lutigest® not statistically different to IM progesterone [0.8 +/- 0.4 (0.2-2.6) and 1.0 +/- 0.25 (0.4-1.0)]
Mean serum progesterone levels during early pregnancy: During early pregnancy, serum progesterone levels were statistically significantly higher in the Lutigest® group on mean days (after oocyte retrieval) of 19-22, 23-26, and 27 days to 12 weeks of gestation.
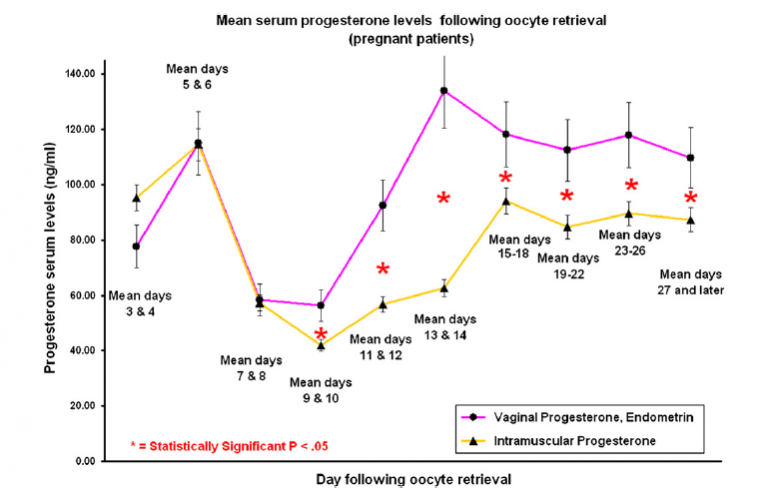
Luteal support with Lutigest® was associated with treatment outcomes that were no different from those associated with IM progesterone.
Job Code: UK-LUG-2300004 - Date of preparation: September 2023